Ke Yang is a Ph.D. candidate at the College of Electrical Engineering, Zhejiang University, advised by Professor Quanyuan Jiang and Professor Guangchao Geng. He received his B.Eng. degree from Zhejiang University in 2021. His research interests focus on the dynamic modeling and stability analysis of modern power systems, as well as the application of machine learning and artificial intelligence in power system dynamics.
He has authored 6 peer-reviewed journal articles, including 4 papers as first author in high-impact publications such as Nature Communications and various IEEE Transactions. He also serves as a reviewer for several leading international and domestic journals, including IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs and CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems.
As a student project lead, he has been deeply involved in multiple research initiatives funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC), State Grid Corporation of China (SGCC), and China Southern Power Grid (CSG). He spearheaded the development of data-driven dynamic models for synchronous generators and renewable energy plants. These research contributions have been successfully implemented in industry-standard simulation platforms, including ADPSS and DSP.
Education
Aug. 2017 - Jun. 2021
-
 Zhejiang UniversityBachelor of Engineering in Electrical Engineering and Its Automation
Zhejiang UniversityBachelor of Engineering in Electrical Engineering and Its Automation
Sep. 2021 - Jun. 2026
-
 Zhejiang UniversityPh.D. in Electrical Engineering
Zhejiang UniversityPh.D. in Electrical Engineering
Advisor: Prof. Quanyuan Jiang & Prof. Guangchao Geng
News (view all )
Selected Publications (view all )
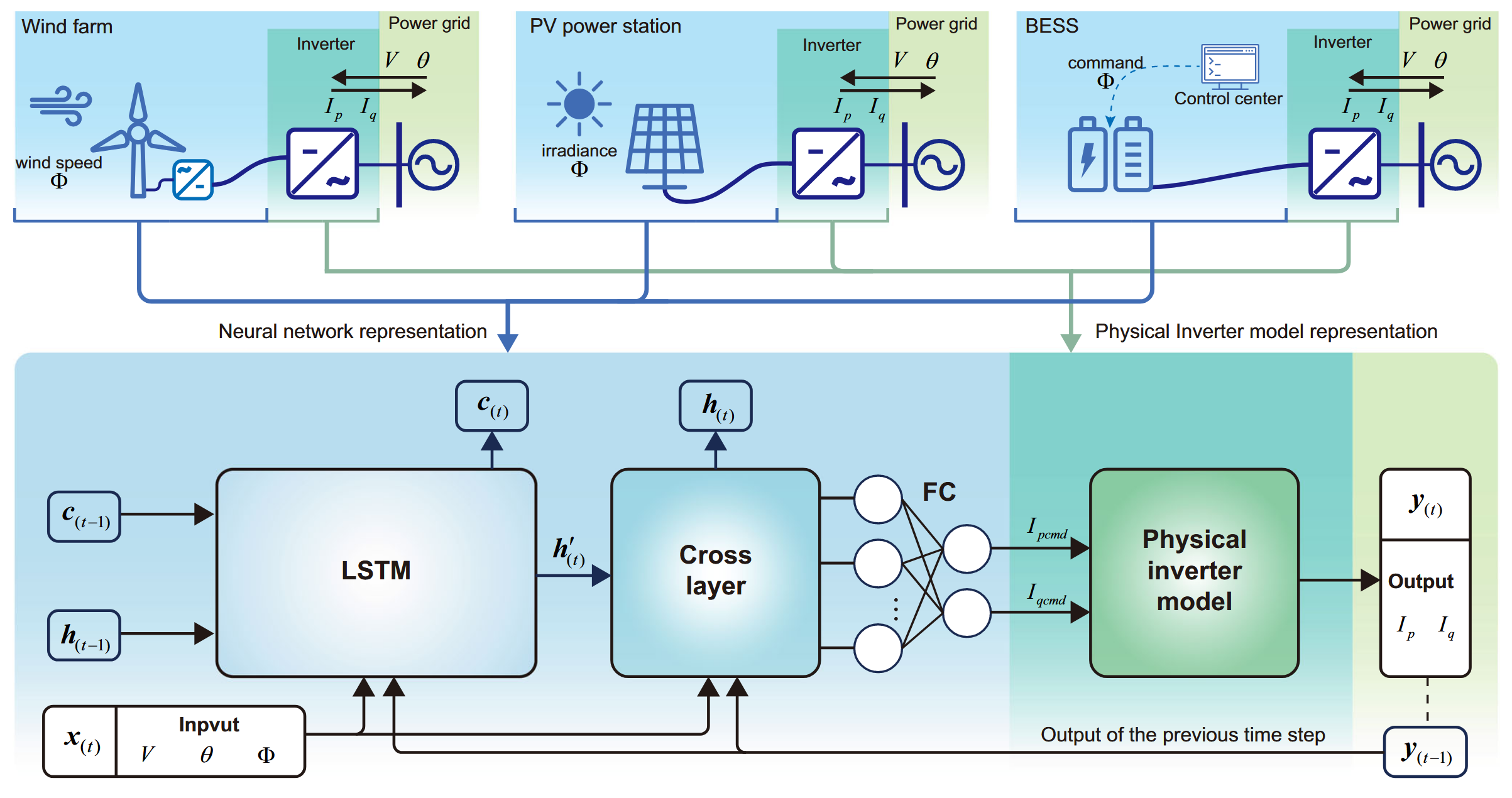
Data-Driven Dynamic Modeling for Inverter-Based Resources Using Neural Networks
Ke Yang, Xin Wang, Xunjun Chen, Renshun Wang, Guangchao Geng*, Quanyuan Jiang ( * corresponding author )
Nature Communications 2025
Data-Driven Dynamic Modeling for Inverter-Based Resources Using Neural Networks
Nature Communications 2025
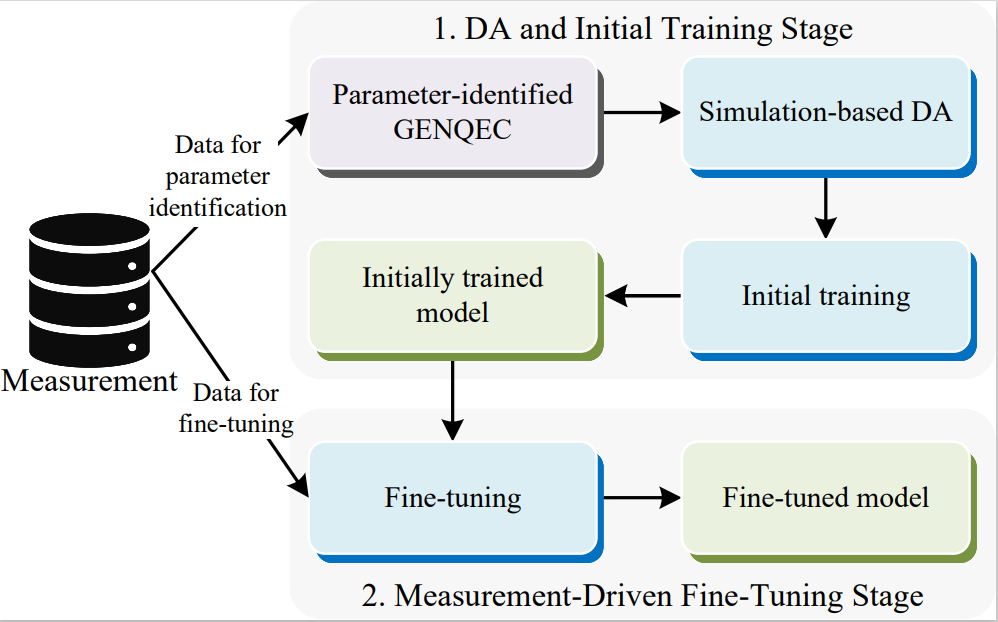
Neural Network-Based Dynamic Modeling of Synchronous Generator Using Data Augmentation
Ke Yang, Xin Wang, Quan Zhang, Renshun Wang, Guangchao Geng*, Quanyuan Jiang ( * corresponding author )
IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2025
Neural Network-Based Dynamic Modeling of Synchronous Generator Using Data Augmentation
IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2025
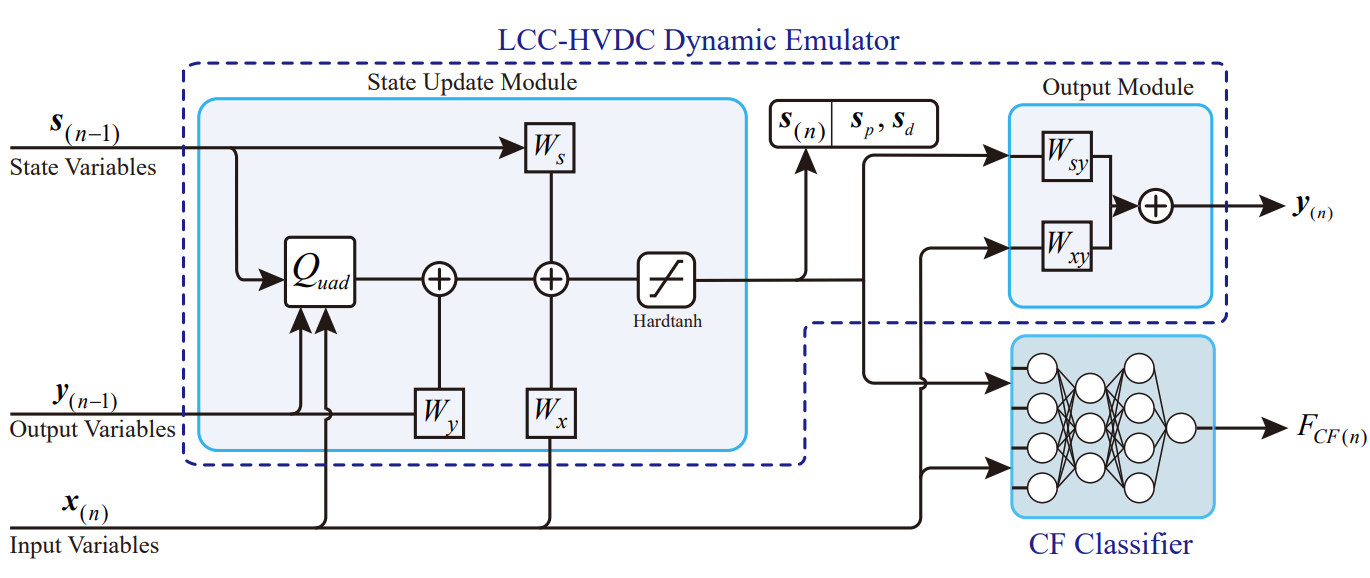
Dynamics Enhanced Quasi-Steady-State Model of LCC-HVDC Systems Based on Neural Network
Ke Yang, Xin Wang, Quan Zhang, Guangchao Geng*, Quanyuan Jiang ( * corresponding author )
IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 2025
Dynamics Enhanced Quasi-Steady-State Model of LCC-HVDC Systems Based on Neural Network
IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 2025
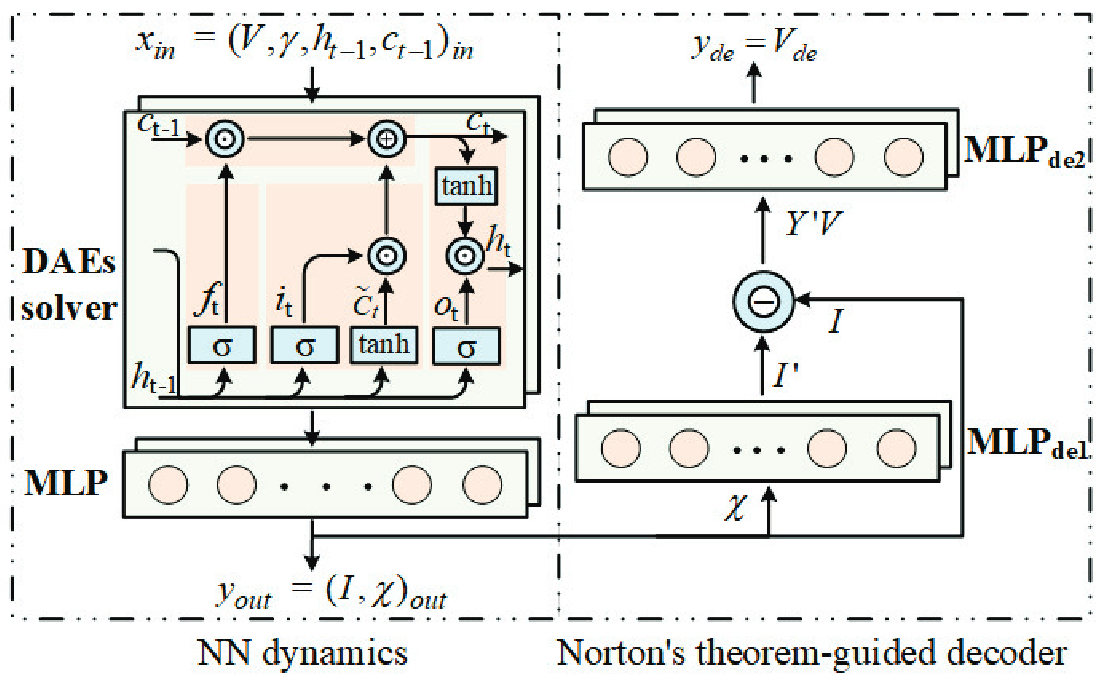
Convergence Enhancement for Neural Network Integrated Power System Time Domain Simulation
Ke Yang, Xin Wang, Guangchao Geng*, Quanyuan Jiang ( * corresponding author )
IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2025
Convergence Enhancement for Neural Network Integrated Power System Time Domain Simulation
IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2025
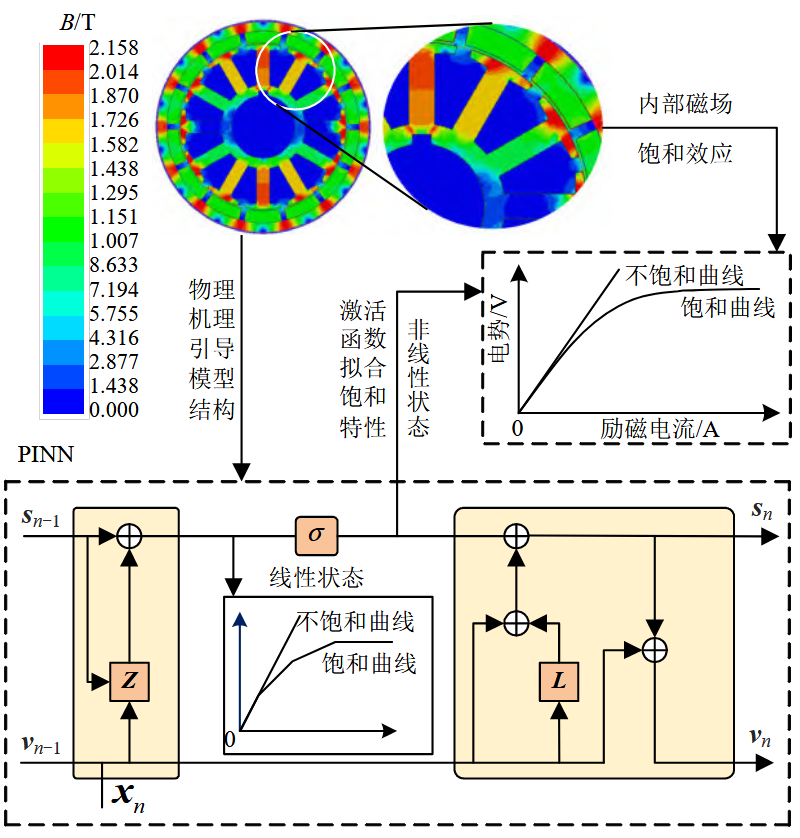
Modeling of Synchronous Generator Based on Physics-informed Neural Network
Ke Yang, Xin Wang, Jiajie Ling, Guangchao Geng*, Quanyuan Jiang ( * corresponding author )
Proceedings of the CSEE 2024
Modeling of Synchronous Generator Based on Physics-informed Neural Network
Proceedings of the CSEE 2024
